T.O. 33B-1-1
3-12
3.1.8.3
Demagnetization.
Ferromagnetic materials subjected to magnetic particle inspection are usually demagnetized following their inspection.
The problem of demagnetization may be easy or difficult depending on the type of material, part geometry, and
magnetic field orientations used. Demagnetization involves subjecting a magnetized part to a continuously reversing
magnetic field that gradually decreases in strength. This action reduces the strength of the residual magnetic field in
the part. Although some residual magnetization will remain, this method can reduce the residual magnetic field to
acceptable levels. Note that materials heated above their Curie temperature become non-magnetic, thus offering
another method of demagnetization.
3.1.8.3.1
There are a number of methods of demagnetization available with varying degrees of effectiveness. They can be
explained with the hysteresis loop shown in Figure 3-16. Nearly all are based on the principle of subjecting a part to a
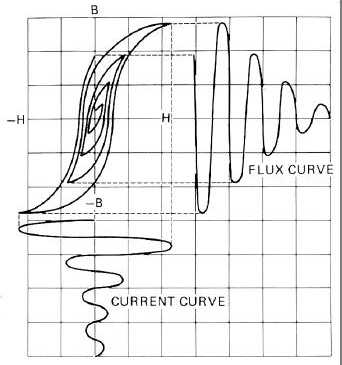
continually reversing magnetic field that gradually reduces in strength down to zero. This is illustrated in Figure 3-17.
The waveform is shown at the bottom of the graph of the reversing current used to generate the hysteresis loops. As the
current diminishes in value with each reversal, the loop shrinks and traces a smaller and smaller path.
3.1.8.3.2
The waveform at the upper right of Figure 3-17 represents the flux in the part as indicated on the diminishing
hysteresis loops. Both current and flux waveforms are plotted against time, and when the current reaches zero the
residual field in the part will also have approached zero. Precautions to be observed in the use of this principle are:
a. Be certain that the magnetizing force is high enough at the start to overcome the coercive force, and to
reverse the residual field initially in the part.
b. The decrease between successive reductions of current is small enough so that the reverse magnetizing
force will be able, on each cycle, to reverse the field remaining in the part from the previous reversal.
Figure 3-17. Flux Waveform During Demagnetization, Projected from the Hysteresis Loop.