(c) Therefore, the peak pressure is approximately 0.9 times 0.6, or 0.54 times the pressure calculated
from the perfect gas law.
55. Initiators. a. The hose-end pressure from an initiator can be estimated from the equation of state, modified to
account for heat losses in the initiator body, at the initiator orifice, and in the aircraft hose.
Where:
Pt = pressure at end of hose
C = charge weight
F = propellant impetus
Vc = initiator volume
Vt = hose volume
β = fraction heat loss in initiator and at initiator orifice
ht = Wheat loss per unit area in hose
St = hose surface area
γ = ratio of specific heats
b. The value of β is generally 0.25 to 0.35, and ht for aircraft hose is on the order of one-tenth to one-fifteenth the
heat loss encountered in guns and propellant actuated devices where the energy transfer is to metal, or about 25 to 30 ft-
2
3
3
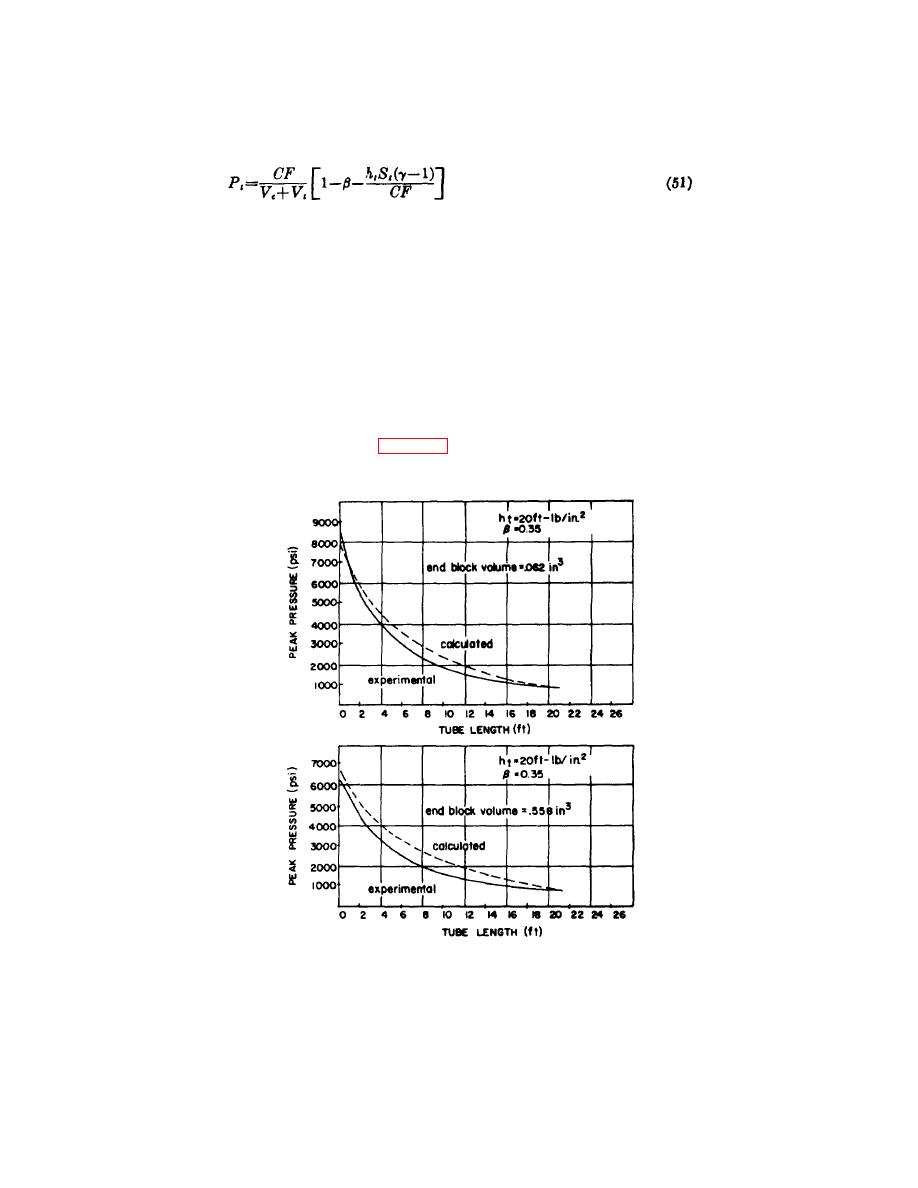
lb/in. . Equation (51) was applied to the M3 initiator to calculate the pressure in 0.062 in. and 0.558 in. end blocks. The
computed and measured pressures are shown in figure 52 as functions of hose length and are in satisfactory agreement.
Figure 52. Relationship of hose pressure and hose length for M3 Initiator.
69


