selected so that they operate throughout this range with
forces, and damping forces (if a damper is used). In
minimum variation in performance. Particular attention
aircraft installations, friction and bending forces may be
must be given to the selection of nonmetallic materials
present in the tubes of catapults and removers as a
which may age and cease to function properly. The
result of aircraft maneuvers and aerodynamic loads.
coefficient of expansion and the viscosity of damping
14. Weight and Size (Envelope). a. Weight and size,
and buffing fluids also are important considerations
although subordinate to reliability, generally are critical
because of this wide temperature range.
considerations in aircraft or missile installations. The
design of the propellant actuated device is dependent
b. Propellant actuated devices are supplied as
upon a specific space allocation, which can result in
sealed units to prevent moisture or dirt entering during
mounting problems, insufficient actuator stroke for the
long storage periods (as long as 3 years either on a
task, and complicated mechanical and ballistic designs.
shelf or mounted in an aircraft). As added insurance,
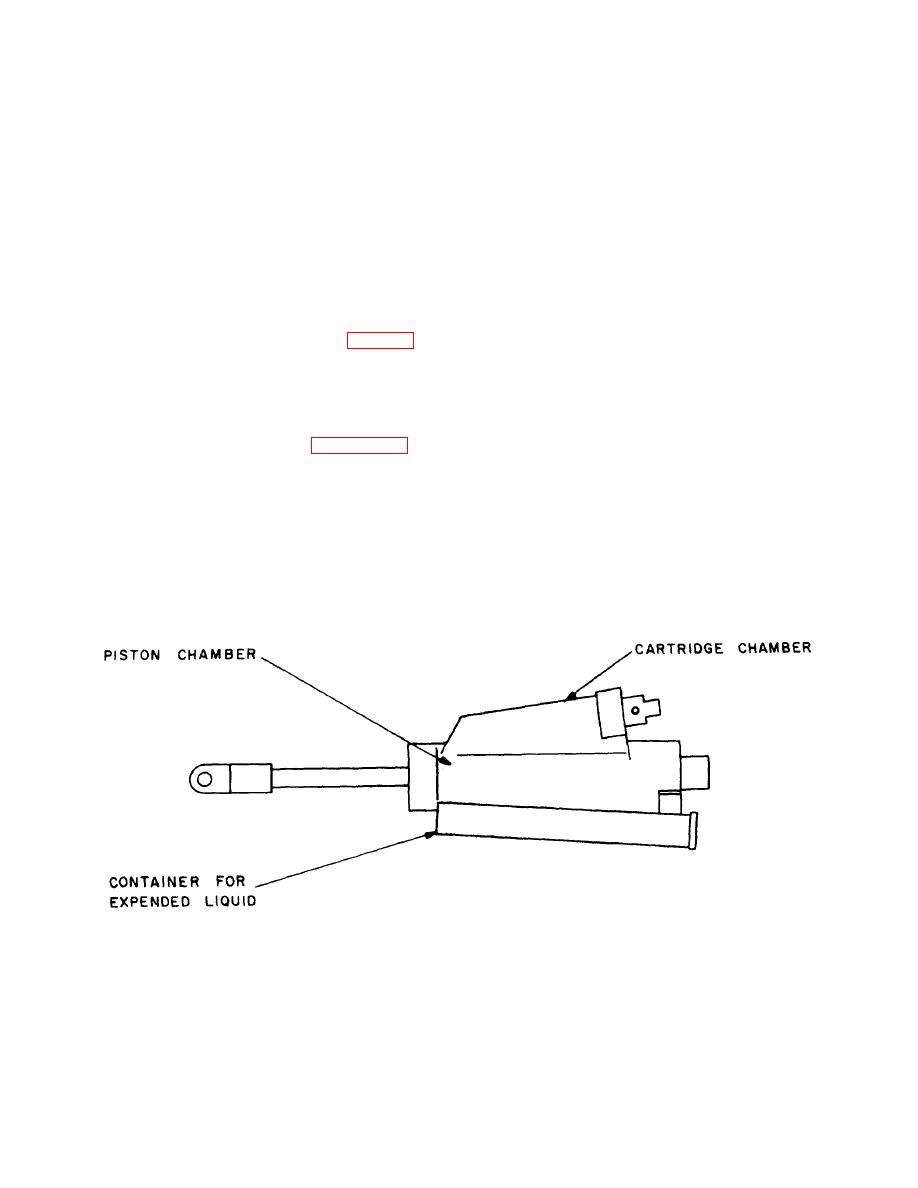
As an example, space limitations can cause a devices
cartridges are hermetically sealed, and are replaced
which could be fabricated easily from a single long tube
periodically to prevent propellant aging from adversely
with piston, chamber, and end connections all on the
affecting performance.
same axis, to be designed with telescoping tubes or in a
c. Threaded connections must be capable of
folded or stacked configuration, as shown in figure 19.
withstanding torque tests as insurance against loosening
b. To reduce weight, it is necessary to operate with
when exposed to vibrations encountered in handling,
working stresses which approach the yield stresses of
shipment, or installation. A Nylok pellet, inserted in the
the materials used. The sizes of the parts are adjusted
threaded joint, creates sufficient friction to prevent
and readjusted to provide safety factors which
loosening, yet the device may be disassembled by
experience has indicated will produce a reliable item.
applying sufficient torque. Staking the threads is not
The safety factors used are covered in paragraph 28.
considered an acceptable way of meeting vibration
(torque) requirements if the device contains a cartridge,
c. The selection of materials for propellant
since the device may require disassembly.
actuated devices entails more than just strength and
weight consideration. Resistance to corrosion, ease of
d. If a propellant actuated device can survive a 6-
fabrication, and resistance to erosion and chemical
foot drop onto concrete, it can withstand the maximum
action with propellants or damper fluids also are factors.
shock which will occur in service. Devices, therefore,
15.
Environment.
a.
In aircraft applications,
are designed to withstand this drop test, which means
propellant actuated devices are exposed to
that the propellant grains will not shatter and the firing
temperatures within the range of -65 to +200 .
F
mechanism will not function as a result of the shock.
Propellant, primers, and all mechanical parts must be
The design of shear pins used to retain the firing pins in
Figure 19. Thruster with stacked configuration.
22


