T.O. 33B-1-1
6-6
6.1.4
Unique Properties of Gamma Rays.
6.1.4.1
General.
Gamma-ray radiography is basically the same as X-ray radiography. Differences in material properties and effects
between X-rays and gamma rays are largely a matter of degree. The major advantage of using gamma rays is the fact
that gamma ray sources are small and provide access to small spaces, thereby simplifying exposure technique.
Exposure periods are, however, generally longer with gamma ray sources.
6.1.4.2
Sources Of Radiation.
Many atoms exhibit a property called radioactivity, which is a phenomenon of spontaneous disintegration or decay.
This characteristic is believed to be caused by the instability of the complex structure of the atom under the action of the
electric, magnetic and gravitational forces existing within. Radium is one of the elements with a natural unbalance that
releases energy in the form of gamma rays to achieve a more stable condition. In addition to the gamma rays, some
alpha particles (helium nuclei) and beta particles (electrons) are allowed to escape. The alpha and beta particles are
readily absorbed, but the gamma rays are more penetrating since their energy extends above 1,000,000 electron volts
(eV). This energy release is uncontrolled and is a result of forces in the atom. Many of the atomic structures can be
artificially made to release energy by subjecting them to strong fields of neutrons generated in nuclear reactors. These
neutron fields add energy to the atom, which upsets the balance within the nucleus and causes the atom to emit one or
more types of energy. Cobalt is one element commonly made artificially radioactive and used in NDI since the energy
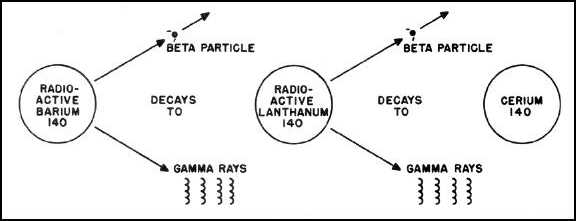
it releases is a very penetrating form of gamma rays. An example of nuclear disintegration and the release of energy is
shown in Figure 6-4.
Figure 6-4. Diagram of Nuclear Disintegration.
SECTION II
X-RAY GENERATORS
6.2
X-RAY GENERATORS.
6.2.1
Definition.
X-ray generators are man-made electronic devices designed to produce X radiation. Many types of X-ray generators
may be obtained commercially. X-ray equipment may be either portable or stationary. Portable X-ray generators are
used for inspection of test objects that are either impossible or very difficult to transport. Stationary X-ray generators
are used in shielded facilities where the objects to be tested can be readily transported to the X-ray equipment.