T.O. 33B-1-1
6-11
6.2.4.2.2
Anode.
As mentioned previously, there must be a target for the electron beam to strike before X-rays are actually produced. In
radiographic tubes the target material is generally made of tungsten. The choice of tungsten as a target for industrial
radiography is based on four material characteristics:
a. High atomic number (74). The higher the atomic number of a material the more efficient is the
conversion from electrical energy into X-ray energy.
b. High melting point (690F*). Most of the energy in the electrons bombarding the target is dissipated in
the form of heat. The extremely high melting point of tungsten permits operation of the target at very
high temperatures.
c. High thermal conductivity. Permits rapid removal of heat from the target, allowing maximum energy
input for a given area size.
d. Low vapor pressure. This reduces the amount of target material vaporized during operation.
6.2.4.2.2.1
The tungsten target material is usually imbedded into a massive copper rod. Copper is an excellent thermal conductor
and is used to remove the heat from the target for dissipation by air, oil, or water cooling, depending on tube design and
operation. The target and its copper support are the anode. To produce X-rays it must be at a positive potential
(voltage) with respect to the cathode in order to attract the electrons available at the cathode.
6.2.4.2.3
Focal Spot.
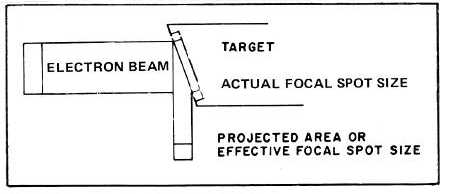
The focal spot is the area of the target that is bombarded by the electrons from the cathode. The shape and size of the
focusing cup of the cathode and the length and diameter of the filament all determine the size and shape of the focal
spot. The size of the focal spot has a very important effect upon the quality of the X-ray image. The smaller the focal
spot the better the detail of the image. The electron stream from the filament is focused as a narrow rectangle on the
anode target. The typical target face is made at an angle of about 20 degrees to the cathode. When the rectangular
focal spot is viewed from below, in the position of the film, it appears more nearly a small square. Thus, effective area
of the focal spot is only a fraction of its actual area (see Figure 6-9). By using the X-rays that emerge at this angle, a
small focal spot is created, improving radiographic definition. Because the electron stream is spread over a greater area
of the target, heat dissipation by the anode is improved.
Figure 6-9. Effective Focal Spot Size.
6.2.4.2.4
Inherent Filtration.
Inherent filtration is the filtration or reduction in radiation energy due to absorption by the material necessary to
provide the vacuum, the electrical insulation, and mechanical rigidity of the X-ray tube. In construction of some glass
X-ray tubes, the port is reduced in thickness to provide less inherent filtration. In some other tubes the port is made of