T.O. 33B-1-1
4-33
4.3.5
Impedance Plane Analysis.
Most eddy current inspection applications have two major problems to overcome. The first is to ignore changes in
parameters not of interest during the test; an example is lift-off variation while inspecting for cracks. The second is to
recognize valid indications while other changes are occurring. Another way of stating this is that variations in a
parameter such as lift-off should not be mistaken for valid defect indications and valid defect indications should not be
hidden by changes in parameters such as lift-off. Impedance plane analysis, also called phase analysis, is a tool that is
effective in solving these problems.
4.3.5.1
Phase Adjustment.
In eddy current instruments with two dimensional displays, the signals displayed can be rotated to align the direction of
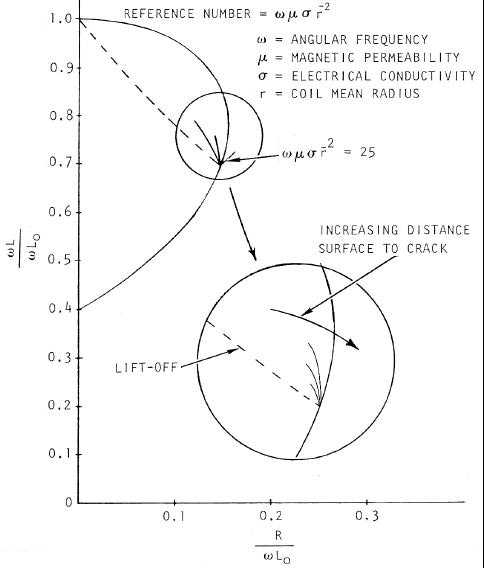
changes caused by the variable of no interest with the horizontal (or vertical, if so desired) axis as shown in Figure 4-
31. This is also called phase adjustment and its purpose is to position the response associated with lift-off variations in
a direction that does not interfere with the interpretation of responses from variables of interest. The effectiveness of
this technique increases as the phase difference between lift-off and the variable of interest increases from 0o to 90o.
Figure 4-31. Impedance Diagram Showing the Effect of a Crack.