T.O. 33B-1-1
6-21
rays is called a radiograph; film exposed by using a radioisotope may be called a gammagraph. The term radiograph is
used throughout this chapter. Films are an excellent recording medium with a very high signal-to-noise ratio and high
amplification. Real-time, radioscopic electronic devices cannot match the excellent recording characteristics of film.
This section describes how films work, reviews how films respond to radiation, and discusses radiographic paper.
6.4.1.2
General Theory of Industrial Radiographic Film.
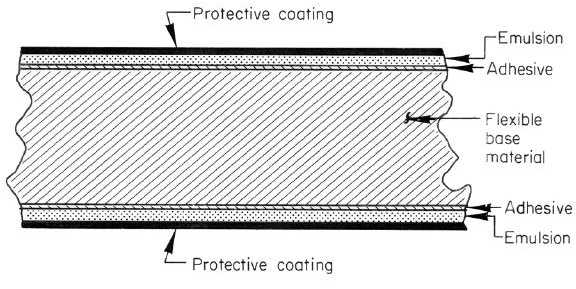
Films consist of a base material coated with an emulsion containing the radiation-sensitive silver-halide crystals, which
are usually silver bromide. Most modern films have a polyester base which is either transparent or has a slightly blue
tint. The polyester is very durable, does not absorb water or processing chemicals, and is dimensionally stable dries
easily, and will not support combustion. Figure 6-11 shows schematically the structure of radiographic films.
Figure 6-11. Sketch of Cross Section of X-Ray Film
6.4.1.2.1
Emulsion.
The emulsion consists of a gelatin material containing an even distribution of the radiation-sensitive silver bromide
crystals or grains. This emulsion is coated on the polyester base in very thin layers, usually about 0.001 inch in
thickness. Most X-ray films have double emulsions, i.e., are coated on both sides of the base material. Since the thin
support material offers very little absorption to the X-rays normally used for industrial applications, the double
emulsions essentially reduce exposure requirements to one-half that required for a single emulsion. However, some
films, intended for radiography in which visibility of the smallest detail is required, have emulsion only on one side.
6.4.1.2.2
Latent Image.
The latent image is formed by interactions of the electromagnetic radiation with the silver bromide crystals. When
solid silver bromide is formed in the manufacture of film, the silver atoms give up an orbital electron to a bromine
atom. Since the silver atoms have given up an electron, they have a positive electrical charge and are silver ions (Ag+).
The bromine atoms have acquired this negative electron and have become bromide ions (Br-). The silver bromide
crystal is a cubical array of the silver and bromine ions. The cubical crystalline structure of the silver bromide crystal is
not perfect; if it were, the photographic process could not exist. Within the crystal lattice structure are extra silver ions
called interstitial ions; these do not occupy a lattice position in the crystal. There are also foreign molecules or
dislocations (distortions) of the crystal array within the crystal, all of which form latent image sites.
6.4.1.2.2.1
The accepted theory of the formation of the latent image (that is, an image which may be revealed by development) in a
photosensitive emulsion is based upon the Gumey-Mott concept of exposure. It is theorized that the formation is a two-