T.O. 33B-1-1
3-24
3.3.4.2.2
The prevailing approach for obtaining direct current for magnetic particle inspection is through rectification of
alternating current using solid state rectifiers. A rectifier (diode) is a device that allows electric current to flow through
it in only one direction. By proper connection of rectifiers, the back and forth flow of alternating current is converted
to a current flow in only one direction. This is a form of direct current. A rectifier circuit, which converts both
alternations (back and forth flow) of the alternating current to one direction of current flow, is called a full-wave
rectifier.
3.3.4.2.3
Single-phase alternating current can be rectified using a full-wave rectifier circuit to obtain direct current for magnetic
particle inspection. Single-phase rectification, however, is seldom used to obtain direct current, except in the case of
small hand-held magnetizing devices. Since three-phase power is so readily available in industry, direct current for
magnetic particle inspection units is usually obtained using three-phase full-wave rectifiers.
3.3.4.3
Comparison Of Results Using Different Types Of Current.
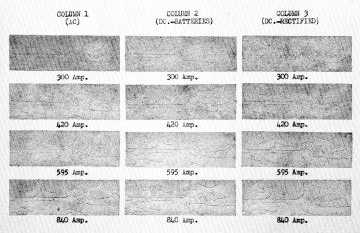
Figure 3-21 is a comparison of indications of the same set of fine surface cracks on a ground and polished piston pin,
obtained by using 60 cycle AC, DC from storage batteries (straight DC), and DC from rectified three-phase 60 cycle
AC respectively. Four values of current were used in each case with a central conductor to magnetize the hollow pin.
The indications produced with AC are heavier than the DC indications at each current level, although the difference is
most pronounced at the lower current values. Straight DC and rectified AC are comparable in all cases. The AC
currents are meter (R.M.S. or Root Mean Square) values, so that peak of cycle currents, and therefore magnetizing
forces, are 1.41 times the meter reading shown.
Figure 3-21. Comparison of Indications of Surface Cracks on a Part Magnetized with AC, DC and Three Phase
Rectified AC
3.3.4.3.1
Another comparison can be made using the Ketos ring specimen, the drawing for which is shown in Figure 3-22. The
specimen, made of unhardened (annealed) tool steel (0.40 percent carbon), is 7/8 inch thick. Holes, 0.07 inch in
diameter and parallel to the cylindrical surface, are located at increasing depths below the surface.